Rolling resistance
Rolling resistance, sometimes called rolling friction or rolling drag, is the resistance that occurs when a round object such as a ball or tire rolls on a flat surface, in steady velocity straight line motion. It is caused mainly by the deformation of the object, the deformation of the surface, or both. Additional contributing factors include wheel radius, forward speed,[1] surface adhesion, and relative micro-sliding between the surfaces of contact. It depends very much on the material of the wheel or tire and the sort of ground.
For example, rubber will give a bigger rolling resistance than steel on some surfaces (polished steel) and a lower rolling resistance on other surfaces (pavement/tarmac). Also, sand on the ground will give more rolling resistance than concrete. Any moving wheeled vehicle will gradually slow down due to rolling resistance including that of the bearings, but a train car with steel wheels running on steel rails will roll farther than a bus of the same mass with rubber tires running on tarmac. The coefficient of rolling resistance is generally much smaller for tires or balls than the coefficient of sliding friction.[2]
Contents |
Primary cause
The primary cause of rolling resistance is hysteresis:
A characteristic of a deformable material such that the energy of deformation is greater than the energy of recovery. The rubber compound in a tire exhibits hysteresis. As the tire rotates under the weight of the vehicle, it experiences repeated cycles of deformation and recovery, and it dissipates the hysteresis energy loss as heat. Hysteresis is the main cause of energy loss associated with rolling resistance and is attributed to the viscoelastic characteristics of the rubber.
- -- National Academy of Sciences[3]
Thus materials that flex more and bounce back slowly, such as rubber, exhibit more rolling resistance than materials that flex less, such as steel, or that bounce back more quickly, such as silica. Low rolling resistance tires typically incorporate silica in place of carbon black in their tread compounds to reduce low-frequency hysteresis without compromising traction.[4]
Factors that contribute in tires
Several factors affect the magnitude of rolling resistance a tire generates:
- As mentioned in the introduction: wheel radius, forward speed, surface adhesion, and relative micro-sliding.
- Material - different fillers and polymers in tire composition can improve traction while reducing hysteresis. The replacement of some carbon black with higher-priced silica–silane is one common way of reducing rolling resistance.[3] The use of exotic nano materials including nano clay has been shown to reduce rolling resistance in high performance rubber tires. Solvents may also be used to swell solid tires, decreasing the rolling resistance.
- Dimensions - rolling resistance in tires is related to the flex of sidewalls and the contact area of the tire[5] For example, at the same pressure, wider bicycle tires flex less in sidewalls as they roll and thus have lower rolling resistance (although higher air resistance).[5]
- Extent of inflation - Lower pressure in tires results in more flexing of sidewalls and higher rolling resistance.[5] This energy conversion in the sidewalls increases resistance and can also lead to overheating and may have played a part in the infamous Ford Explorer rollover accidents.
- Over inflating tires (such a bicycle tires) may not lower the overall rolling resistance as the tire may skip and hop over the road surface. Traction is sacrificed, and overall rolling friction may not be reduced as the wheel rotational speed changes and slippage increases.
- Sidewall deflection is not a direct measurement of rolling friction. A high quality tire with a high quality (and supple) casing will allow for more flex per energy loss than a cheap tire with a stiff sidewall. Again, on a bicycle, a quality tire with a supple casing will still roll easier than a cheap tire with a stiff casing. Similarly, as noted by Goodyear truck tires, a tire with a "fuel saving" casing will benefit the fuel economy through many tread lives (i.e. retreading), while a tire with a "fuel saving" tread design will only benefit until the tread wears down.
- In tires, tread thickness and shape has much to do with rolling resistance. The thicker and more contoured the tread, the higher the rolling resistance[5] Thus, the "fastest" bicycle tires have very little tread and heavy duty trucks get the best fuel economy as the tire tread wears out.
- Hard steel rails last longer than rubber tires, but have lower static friction (traction). They may also suffer fatigue cracking because the cracked area is not worn away by the passing trains.
- Smaller wheels, all else being equal, tend to have higher rolling resistance than larger wheels. However, in some laboratory tests, smaller wheels appeared to have similar or lower losses than large wheels,[6] but these tests were done rolling the wheels against a small-diameter drum, which would theoretically remove the advantage of large-diameter wheels, thus making the tests irrelevant for resolving this issue. Virtually all world speed records have been set on relatively narrow wheels, probably because of their aerodynamic advantage at high speed, which is much less important at normal speeds.
- Temperature: with both solid and pneumatic tires, rolling resistance has been found to decrease as temperature increases (within a range of temperatures: i.e. there is an upper limit to this effect)[7]
Measurement
There are at least two popular models for calculating rolling resistance.
- "Rolling resistance coefficient (RRC). The value of the rolling resistance force divided by the wheel load. The Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) has developed test practices to measure the RRC of tires. These tests (SAE J1269 and SAE J2452) are usually performed on new tires. When measured by using these standard test practices, most new passenger tires have reported RRCs ranging from 0.007 to 0.014."[3] In the case of bicycle tires, values of 0.0025 to 0.005 are achieved.[8] These coefficients are measured on rollers, with power meters on road surfaces, or with coast-down tests. In the latter two cases, the effect of air resistance must be subtracted or the tests performed at very low speeds.
- The coefficient of rolling resistance b, which has the dimension of length, is approximately (due to the small-angle approximation of
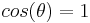 ) equal to the value of the rolling resistance force times the radius of the wheel divided by the wheel load.[1]
) equal to the value of the rolling resistance force times the radius of the wheel divided by the wheel load.[1] - ISO 8767 is used to test rolling resistance in Europe.
The results of these tests can be hard for the general public to obtain as manufacturers prefer to publicize "comfort" and "performance".
Physical formula
The force of rolling resistance, not adjusted for velocity, can be calculated by[3]:
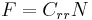
- where
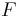 is the rolling resistance force (shown in figure 1),
is the rolling resistance force (shown in figure 1),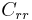 is the dimensionless rolling resistance coefficient or coefficient of rolling friction (CRF), and
is the dimensionless rolling resistance coefficient or coefficient of rolling friction (CRF), and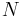 is the normal force (equal to W, not R, as shown in figure 1).
is the normal force (equal to W, not R, as shown in figure 1).
The power required to overcome this rolling resistance at a given velocity can be expressed as:
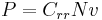
- where
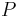 is the power required,
is the power required,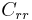 is the dimensionless rolling resistance coefficient or coefficient of rolling friction (CRF), and
is the dimensionless rolling resistance coefficient or coefficient of rolling friction (CRF), and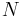 is the normal force (equal to W, not R, as shown in figure 1).
is the normal force (equal to W, not R, as shown in figure 1).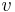 is the forward speed,
is the forward speed,
The coefficient of rolling friction for a slow rigid wheel, not adjusted for velocity, can be calculated by[1][2]
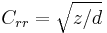
- where
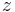 is the sinkage depth
is the sinkage depth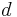 is the diameter of the rigid wheel
is the diameter of the rigid wheel
The force of rolling resistance can also be calculated by[1]:
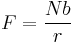
- where
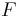 is the rolling resistance force (shown in figure 1),
is the rolling resistance force (shown in figure 1),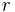 is the wheel radius,
is the wheel radius,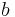 is the rolling resistance coefficient or coefficient of rolling friction with dimension of length, and
is the rolling resistance coefficient or coefficient of rolling friction with dimension of length, and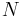 is the normal force (equal to W, not R, as shown in figure 1).
is the normal force (equal to W, not R, as shown in figure 1).
Equating the above two equations, and solving for b, gives b = Crr·r. Therefore, if a source gives rolling resistance coefficient (Crr) as a dimensionless coefficient, it can be converted to b, having units of length, by multiplying Crr by wheel radius r.
In usual cases, the normal force on a single tire will be the mass of the object that the tires are supporting divided by the number of wheels, plus the mass of the wheel, times the gravitational acceleration (9.81 m·s−2 on earth). In other words, the normal force is equal to the weight of the object being supported, if the wheel is on a horizontal surface.
The above equations don't include variation of rolling resistance with speed. This is a reasonable simplification but measurements at different speeds show some variation.[9]
Rolling resistance coefficient examples
Table of rolling resistance coefficient examples: [2]
| Crr | b | Description |
| 0.0002 to 0.0010[10][11] | 0.5 mm[1] | Railroad steel wheel on steel rail |
| 0.1 mm[1] | Hardened steel ball bearings on steel | |
| 0.0022 to 0.005 [12] | production bicycle tires at 120 psi (8.3 bar) and 50 km/h (31 mph), measured on rollers | |
| 0.0025[13] | Special Michelin solar car/eco-marathon tires | |
| 0.005 | Tram rails standard dirty with straights and curves | |
| 0.0055 [13] | Typical BMX bicycle tires used for solar cars | |
| 0.0062 to 0.015 [14] | Car tire measurements | |
| 0.010 to 0.015[15] | Ordinary car tires on concrete | |
| 0.3[15] | Ordinary car tires on sand |
For example, in earth gravity, a car of 1000 kg on asphalt will need a force of around 100 newtons for rolling (1000 kg × 9.81 m/s2 × 0.01 = 98.1 N).
Effects
Rolling friction generates heat and sound (vibrational) energy, as mechanical energy is converted to these forms of energy due to the friction. One of the most common examples of rolling friction is the movement of motor vehicle tires on a roadway, a process which generates sound and heat as by-products.[16] The sound generated by automobile and truck tires as they roll (especially noticeable at highway speeds) is mostly due to the percussion of the tire treads, and compression (and subsequent decompression) of air temporarily captured within the treads. The heat generated raises the temperature of the frictional surface; moreover, this temperature increase typically increases the coefficient of friction.[17] This is why automobile racing teams preheat their tires.
See also
- Coefficient of friction
- Maglev (Magnetic Levitation, the elimination of rolling and thus rolling resistance)
- Rolling element bearing
References
- ^ a b c d e f Hibbeler, R.C. (2007). Engineering Mechanics: Statics & Dynamics (Eleventh ed.). Pearson, Prentice Hall. pp. 441–442.
- ^ a b Peck, William Guy (1859). Elements of Mechanics: For the Use of Colleges, Academies, and High Schools. A.S. Barnes & Burr: New York. p. 135. http://books.google.com/books?id=orMEAAAAYAAJ&pg=PA135&lpg=PA135&dq=%22rolling+friction%22+%22less+than%22+%22sliding+friction%22&source=web&ots=Exv1A-tzPY&sig=ahIJxiBE4KU-_wTnD1uPWKXA5WE. Retrieved 2007-10-09.
- ^ a b c d "Tires and Passenger Vehicle Fuel Economy: Informing Consumers, Improving Performance -- Special Report 286. National Academy of Sciences, Transportation Research Board, 2006". http://onlinepubs.trb.org/onlinepubs/sr/sr286.pdf. Retrieved 2007-08-11.
- ^ http://www.tyres-online.co.uk/technology/silica.asp
- ^ a b c d "Schwalbe Tires: Rolling Resistance". http://www.schwalbetires.com/tech_info/rolling_resistance.
- ^ "Greenspeed test results.". http://www.legslarry.beerdrinkers.co.uk/tech/GS.htm. Retrieved 2007-10-27.
- ^ http://www.recumbents.com/mars/pages/proj/tetz/other/Crr.html
- ^ http://www.biketechreview.com/tires/AFM_tire_crr.htm
- ^ http://www.recumbents.com/wisil/tetz/coast_measurements.htm
- ^ Gordon, David W. Bicycling Science. Cambridge, Mass. : MIT Press (c. 2004)
- ^ Williams, John A. Engineering Tribology. New York : Cambridge University Press (2005)
- ^ http://www.biketechreview.com/tires/images/AFM_tire_testing_rev8.pdf
- ^ a b Roche, Schinkel, Storey, Humphris & Guelden, "Speed of Light." ISBN 0 7334 1527 X
- ^ Green Seal 2003 Report
- ^ a b Gillespie ISBN 1-56091-199-9 p117
- ^ [1] C. Michael Hogan, Analysis of Highway Noise, Journal of Soil, Air and Water Pollution, Springer Verlag Publishers, Netherlands, Volume 2, Number 3 / September, 1973
- ^ Gwidon W. Stachowiak, Andrew William Batchelor, Engineering Tribology, Elsevier Publisher, 750 pages (2000) ISBN 0750673044